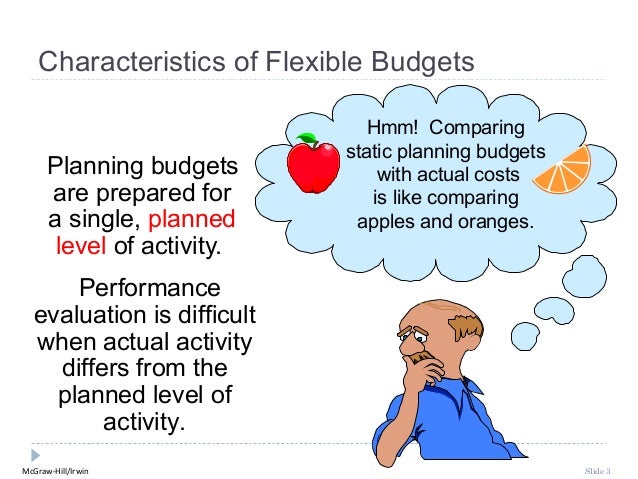
A marketing
channel is the people, organizations, and activities
necessary to transfer the ownership of goods from the point of production to
the point of consumption. It is the way products and services get to the
end-user, the consumer; and is also known as a distribution channel.
Understanding how Marketing Channel Members add Value to Marketing
Process
There
are two forms of marketing channels, direct and indirect. Direct channels sell
products directly to consumers and have no intermediary levels. Indirect
channels sell their products through intermediary levels and do not deal with
consumers.
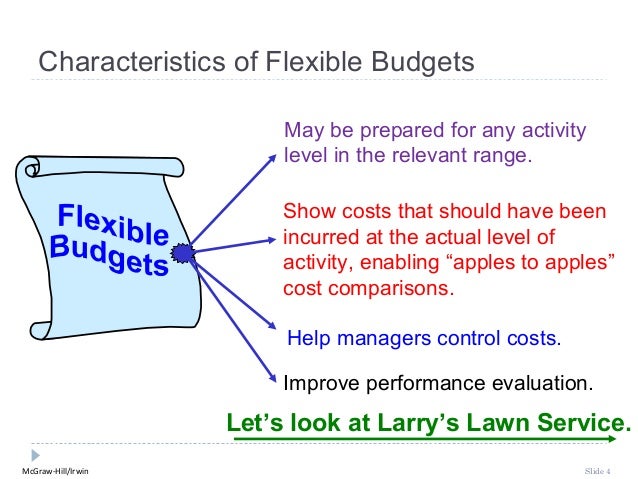
Channel
members consists of retailers and distributors. They purchase manufactured
goods in bulk, and offer them to consumers in broad varieties. As a result,
consumers are able to purchase small assortments of products that are produced
in large quantities. An example of this, is when we purchase toothpaste.
Manufactures produce thousands of pounds of toothpaste, which they provide to
retail stores. Retail stores make single tubes available for purchase because
consumers only desire a small quantity of the specific product at a time. Below
is a graphic of the products and the process to the consumer.
Channel
members perform many functions that add value to consumers. These functions
are:
§
Gather Information and Distribute it
§
Develop Persuasive Communications on
Offerings
§
Communicate with Buyers
§
Shape Offers to Meet Consumer Needs
§
Negotiate Prices
They
also perform functions to assist transactions:
§
Physical Distribution
§
Financing
§
Risk Taking
(Kotler)
Channels
members make good available to markets that desire the products by assisting
companies who cannot do so on their own. Having channel members perform the
functions stated above, consumers are able to purchase products in the desired
quantities at a price they are willing to pay.
Channel Levels – Consumer and industrial marketing
channels
Channel levels consist of consumer
marketing channels or the industrial marketing channels. A
factor common among both channel levels is that both include the producer as
well as the end customer.
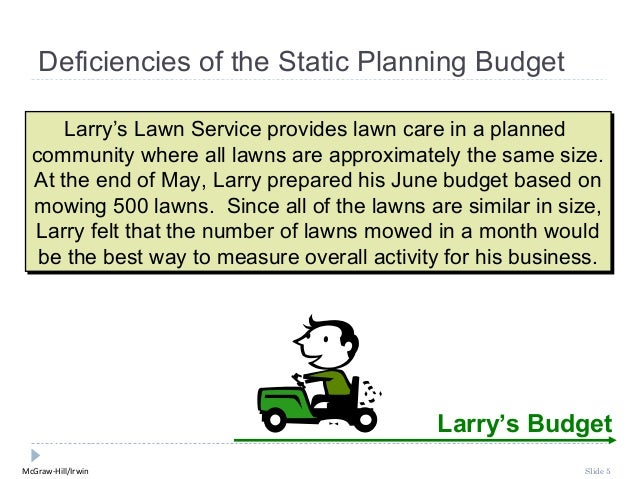
1) Zero Level
channel / Direct Marketing Channel
Consists of a
manufacturer directly selling to the end consumer. This might mean door to door
sales, direct mails or telemarketing. Dell online
sales is a perfect example of a zero level channel marketing.
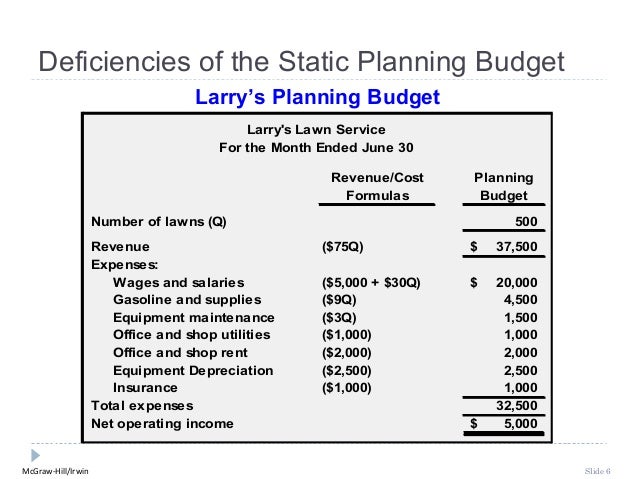
2) One Level
channel
As the name
suggests, the one level channel has an intermediary in between the producer and
the consumer. An example of this can be insurance in which there is an
insurance agent between the insurance company and the customer. Even E-commerce is an excellent
one channel level example – wherein the companies tie up directly with
E-commerce portals and then sell in the market.
3) Two level
Channel
Two level
channel involves the movement of goods from the
company to an intermediary, from from the intermediary to another and then to
customer. This is also commonly known as “breaking the bulk” in FMCG market. A
widely used two level marketing channel especially in the FMCG and
the consumer durables industry which consists of a wholesaler and a retailer.
So the goods go from company to distributor, distributor to retailer and
retailer to consumer.
4) Three level
channel
Again observed
in both the FMCG and the consumer durables industry, the three level channel
can combine the roles of a distributor on top of a dealer and a retailer. The
distributor stocks the most and spreads it to dealers who in
turn give it to retailers.
In the three
level channel, the example can be taken of Ice cream market. Because of the
manufacturing levels required, Ice cream markets have C&F agents
who stock the ice cream in refrigerated cold rooms. These ice creams are then
transported to local distributors who also have refrigerated cold rooms. The
distributors then transport to local dealers who will have 10-12 small
freezers. And finally it is transported to the retailer who will have 1-2
freezer of each company.
Here are perfect
representations for channel levels between consumer marketing channel and an
industrial marketing channel.